Introduction
As an example of connecting to a Mimer SQL database server using ODBC we will use the iODBC product, an ODBC Driver Manager. To verify the connection setup, we are going to use a demonstration program delivered with iODBC called odbctest.
In this article the macOS platform is used.
Description
Verify or install iODBC
iODBC is not a standard part of a macOS installation but a third-party package that has to be installed separately. The installation program can be downloaded from https://www.iodbc.org/ – look under “Downloads” for macOS.
Once installed the iODBC package will be present in the Applications folder as a subfolder iODBC with the administration program, as well as the library components which are all installed in the system library folder structure.
In order to test iODBC with Mimer SQL there has to be a database present on the system and in this example will we use a database named “mimerdb” so that has to be created before continuing with this example. Please note that it is not enough to have a database installed, it has to be installed after iODBC is installed to be added to the ODBC configuration.
(For details as to how to install Mimer SQL and how to create a database, please see the knowledge base article Installing Mimer SQL on macOS. In order to make a database available from iODBC, please make sure that the checkbox for ODBC is marked before creating the database.)
The ODBC Environment
In the iODBC folder under Applications there are several utilities, one of which is the ODBC Administrator. This program is available in two versions, one for 32-bit applications and one for 64 bits, and is used to create, edit and delete ODBC definitions. It also displays which ODBC drivers are installed on the system.
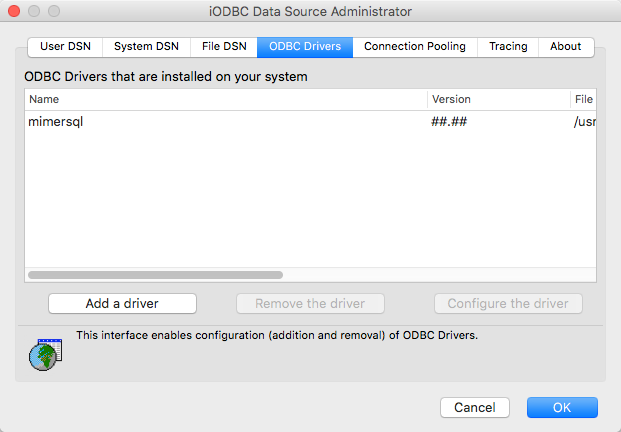
If a Mimer SQL Database Server was installed properly you should have a Driver definition for Mimer ODBC visible in the Drivers tab:
You should also have a data source defined. Click the System DSN button to see the list of available Data Source:
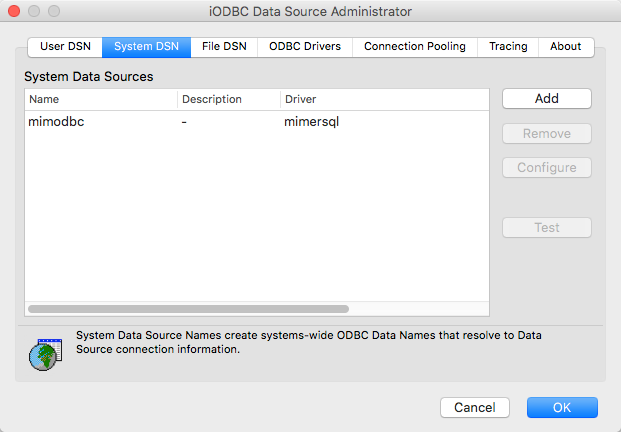
If you want to add a Mimer ODBC Data Source manually, click the Add button in the screen shown above. Select a Mimer ODBC driver in the Drivers list and press OK. You will now get a dialog where you should give a name and description for your data source. Do that and then press the Add button in the same window. Enter the Keyword “Database” by a double-click on “Key”, press the tab key and enter the name of your Mimer SQL database as Value. Please note that you must unlock the ODBC Administrator, by using the locker icon in left down corner, to be able to do any modifications.
Verify your ODBC setup
When Mimer SQL is installed properly and a Mimer SQL database server is installed and registered in the ODBC environment, open up a Terminal application window so that you get a system prompter. The Terminal application is found in /Applications/utilities. Start the odbctest program (or iodbctest and iodbctestw, for wide characters, in later versions), the iODBC Demonstration program, and use the database name for the database that you created earlier. In the following sample session, the mimserver database name and the SYSADM user (with the password chosen when the database was created) are used:
# odbctest
iODBC Demonstration program
This program shows an interactive SQL processor
Enter ODBC connect string (? shows list): ?
DSN | Description
---------------------------------------------------------------
mimdb | mimersql
Enter ODBC connect string (? shows list): DSN=mimdb
Data source name [mimserver]: mimdb
Username []: sysadm
Password []:
Driver: 10.01.0004
SQL> select cast(object_name as char(25)), object_type from system.objects
where object_type = 'BASE TABLE'
|OBJECT_TYPE
-------------------------+--------------------
API_FUNCTION |BASE TABLE
AST_CODES |BASE TABLE
AST_SOURCES |BASE TABLE
CHAR_SETS |BASE TABLE
CHECK_CONSTRAINTS |BASE TABLE
COLLATE_DEFS |BASE TABLE
COLLATIONS |BASE TABLE
COLUMNS |BASE TABLE
COLUMN_OBJECT_USE |BASE TABLE
COLUMN_PRIVILEGES |BASE TABLE
DATABANKS |BASE TABLE
DOMAINS |BASE TABLE
DOMAIN_CONSTRAINTS |BASE TABLE
EXEC_STATEMENTS |BASE TABLE
FIPS_FEATURES |BASE TABLE
FIPS_SIZING |BASE TABLE
KEY_COLUMN_USAGE |BASE TABLE
LEVEL2_RESTRICT |BASE TABLE
LEVEL2_VIEWCOL |BASE TABLE
LEVEL2_VIEWRES |BASE TABLE
MANYROWS |BASE TABLE
MESSAGE |BASE TABLE
MODULES |BASE TABLE
OBJECTS |BASE TABLE
OBJECT_COLUMN_USE |BASE TABLE
OBJECT_OBJECT_USE |BASE TABLE
ONEROW |BASE TABLE
PARAMETERS |BASE TABLE
REFER_CONSTRAINTS |BASE TABLE
ROUTINES |BASE TABLE
SCHEMATA |BASE TABLE
SEQUENCES |BASE TABLE
SERVER_INFO |BASE TABLE
SEVERITY |BASE TABLE
SOURCE_DEFINITION |BASE TABLE
SPECIFIC_NAMES |BASE TABLE
SQL_CONFORMANCE |BASE TABLE
SQL_LANGUAGES |BASE TABLE
STATEMENT_DESCRIPTORS |BASE TABLE
STATEMENT_ROUTINE_USE |BASE TABLE
SYNONYMS |BASE TABLE
TABLES |BASE TABLE
TABLE_CONSTRAINTS |BASE TABLE
TABLE_PRIVILEGES |BASE TABLE
TABLE_TYPES |BASE TABLE
TRANSLATIONS |BASE TABLE
TRIGGERED_COLUMNS |BASE TABLE
TRIGGERS |BASE TABLE
TYPE_INFO |BASE TABLE
USAGE_PRIVILEGES |BASE TABLE
USERS |BASE TABLE
USER_DEF_TYPES |BASE TABLE
VIEWS |BASE TABLE
result set 1 returned 53 rows.
SQL> quit
Have a nice day.
#
Note! The error message “Dialog failed” will be received if the ODBC connect string is not given in the format “DSN=mimdb”.
The Mimer ODBC Driver and the DSN is automatically installed in system wide locations, i.e /Library/ODBC. In some situations it may be necessary to define the ODBCINI environment variable to get access to these definitions:
# export ODBCINI=/Library/ODBC/odbc.ini